Transport Options in Singapore
There are many modes of public transport in Singapore: bus, MRT, taxi and private ride-hail (e.g., Grab). Whilst providing a good range of choices, the method by which fares are charged can be very confusing.
For example, bus fares start with a base fare of $0.80, but will increase proportionately at $0.03 per km up to a maximum of $2.00. On the other hand, taxi fares incur a booking charge of $3.50 plus a base fare of $3.30. The metered fare adds on a variable charge of $0.22 for every 400m. And there is a surcharge of 25% during peak hours between 6 am and 9:30 am, and 6 pm to 12 am after which there is a midnight surcharge of 50%. Ride-hailing services such as Grab uses a simpler fare model. The base fare is $3.00 and there is a variable charge of $0.80 per km. Ride-hailing also includes peak-hour surge pricing of 1.2 times the regular fare. The ride-hailing fare model is opaque to the customer because the app calculates the total and presents it as a “fixed” fare to the customer at the point of booking.
Clearly, the cheaper options are less convenient. For buses, there is a need to walk to the nearest bus stop. Then there is a waiting time of about 25 minutes and the average bus speed is only 40 kph. Taxis and Ride-hail cars are faster at 60 kph. Average waiting time for taxi is 15 minutes while that for Ride-hail is 10 minutes.
Like most commuters in Singapore, Ng Chun Seng uses a variety of these modes of transport depending on his travel needs. However, out of habit and convenience, he tended to use ridehail more than the others. This has led to a sizeable monthly expense on transport. He often wonders if there is a more practical and economical way of choosing the various modes of transport.
Ng Chun Seng works for Clarity Audit Pte Ltd, a local audit and accounting firm which has weekly needs to deliver and collect business documents from its clients. The firm has been using a courier service that charges $26 for every block of 20 km travelled in a week. With the advent of ride-hail, it is now considering whether it should change to other options.
Grab, a local ride-hail company, has offered an attractive corporate package to Clarity based on weekly mileage travelled on its ride-hailing platform. There will be no base charge. All trips will be charged on a per km rate. The rate starts at $1.10 per km. Better rates will be given depending on total weekly mileage as shown in the table below.
Total Weekly Mileage Rate per km
Less than 500 km $1.10
500 km and above $1.00
1,000 km and above $0.90
1,500 km and above $0.80
At the same time, Merlion Car Rental has offered to lease a car to Clarity for just $600 per week, inclusive of insurance, road tax and vehicle maintenance charges. Clarity will have to pay for petrol consumption. The car to be leased has a consistent fuel consumption of 12 to 14 km per litre. Petrol price is presently $2.50 and is expected to be stable for a prolonged period. With a leased car, the company will have greater flexibility to run its document delivery and collection errands.
The CEO of Clarity Audit is unsure whether he should continue with the current courier service or switch to one of the other two options. With the company’s transport needs fluctuating from week to week, there is some uncertainty over the weekly mileage. Nevertheless, recent historical records from the accounting department shows that weekly mileage is about 750 km 30% of the time, 760 km 40%, and 800 km 30%.
Chun Seng is amused that his company is also looking to reduce its travel expenses. In car-lite Singapore, the ability to manage travel costs can be an important competitive advantage.
For the analyses in this case, MRT will not be considered because it has only limited coverage island-wide. The time to walk to a bus stop can also be ignored. For a more equitable comparison between taxi and ride-hail, the analyses shall assume that requests for all taxi rides are by booking.
Stuck with a lot of homework assignments and feeling stressed ? Take professional academic assistance & Get 100% Plagiarism free papers
Question 1
This assignment requires you to practise principles of correct spreadsheet construction and design to help Chun Seng understand and make strategic transport decisions for his company.
Compose a model to analyse the most suitable form of public transport based on travelling time requirements and cost. You may structure your model as follows.
(a) Demonstrate a Rates Table with the following columns:
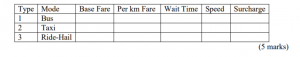
(b) Develop a separate table to compare fares and trip times for the 3 modes of transport (viz bus, taxi and ride-hail) based on distance in km travelled. Apply relevant computations and functions to this table. Your table may have the following columns. Assume that travel is during non-peak hours.
![]()
Add a column to show which mode is the most expensive. This column should either display “Taxi” or “Ride-Hail”. Chun Seng does not expect to travel beyond 30 km for any one trip.
If Chun Seng needs to make a trip of 20 km within a time allowance of 45 minutes, explain what mode of transport you would recommend for him.
(Hint: Trip time includes wait time and vehicle travel time.)
(15 marks)
(c) On a particular day, Chun Seng needs to run an errand at 8:30 am with the following trips in sequence:
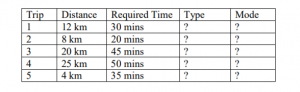
Solve the above commute problem based on the criteria described below.
(i) Using Solver, determine what mode of travel he should choose for each trip in order to achieve the lowest cost to complete all trips on time. Be sure to document the objective and all constraints.
(ii) How much does the total journey cost? At what time will he complete all the
trips?
(iii) What is the total journey cost to complete all trips in the shortest possible time? Is this also the most expensive cost for the entire journey?
(Hint: You may need to add additional columns. Useful functions include vlookup() and time(). Consider the use of Solver with Evolutionary method. Peak and non-Peak hours will also need to be considered. Midnight charges can be ignored as all trips will be made between 6 am and 11:59 pm.)
(20 marks)
Question 2
Compose a model to help Clarity make a decision on its transportation needs. The model should compare the weekly cost for the existing courier service against the two new options of Merlion car leasing and Grab ride-hailing. The comparison shall be based on different weekly mileage travelled. Your model will likely include a table with at least these headings, along with other model parameters clearly presented. You are expected to demonstrate how to look up appropriate parameters needed for computation. You may assume the weekly Mileage (km) is between 0 to 850 km.
![]()
(a) You are expected to demonstrate correct spreadsheet construction and design and apply modelling skill to solve this business problem.
(15 marks)
(b) Using your model, implement tradeoff analysis by analysing the following decisions.
(i) For a weekly mileage of 200km, what would be the courier, car leasing and ridehail costs? (5 marks)
(ii) At what weekly mileage will a leased car be more cost-effective than ridehailing? Add conditional formatting to your model so that the appropriate row to answer
(b)(ii) is automatically highlighted in YELLOW. (10 marks)
(iii) Which transport service would you recommend to the CEO? Use your model to justify and explain why. (10 marks)
Question 3
Using your experience of running a virtual company in MonsoonSIM,
(a) Explain three (3) ways of how you can increase the revenue of your company by showing some performance indicators from Finance, Retail and B2B.
(b) Demonstrate how the organization manage risks and give a detailed explanation of your recommendations.
(Limit your answer to 500 words). (20 marks)
Buy Custom Answer of This Assessment & Raise Your Grades
SingaporeAssignmentHelp.com offers excellent business management assignment help services for all the learners pursuing this academic course. We have the best professionals working with us that hold great academic qualifications and offers excellent university assignment help services.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- BUS306 Risk Assessment Case Study: Outback Retail Ltd Audit Strategy and Substantive Testing Plan
- PSB6013CL Digital Marketing Strategies Project: Exploring Consumer Purchase Intentions in the Fashion E-Commerce Industry
- FinTech Disruption Assignment Report: Case Study on Digital Transformation in Financial Services Industry
- Strategic Management Assignment : Netflix vs Airbnb Case Analysis on Competitive Strategy and Innovation
- Strategic Management Assignment Report: Unilever Case Study on Industry Analysis and Growth Strategy
- PSB6008CL Social Entrepreneurship Assignment Report: XYZ Case Study on Innovation and Sustainable Impact
- MBA Financial Management Global Case Study Assignment: Corporate Valuation & Investment Analysis
- CM1040 Web Development Presentation: Connecting Responsive Design with Data Security
- 7WBS2009 Financial Management Assignment Report: Ratio Analysis and Investment Decision for Alpha and Beta plc
- PSB7003CL Entrepreneurship and Innovation Assignment Report: CW2 Analysis of Organisational Practices and Strategic Innovation Implementation

