| University | National University of Singapore (NUS) |
| Subject | Physics |
Assignment Details:
Question 1
(a) Consider two equal point charges separated by a distance d. If a third test charge is inserted at a point exactly midway between the two charges, what is the amount of net force the third charge would experience?
(b) State what happens when:-
i. Two like charges are brought into close proximity to each other.
ii. Two, unlike charges, are brought into close proximity to each other.
(c) State the units for resistivity and for current density.
(d) If the electric potential at a distance of 5cm from an isolated positive point charge is +100V, determine the magnitude of this charge. Use the given formula.
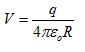
(e) A rectangular carbon block with its dimension is shown in Figure 1.
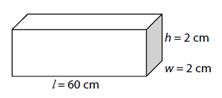
Figure 1
Given the resistivity of carbon at 20°C is ρ=3.5×10-5Ωm, calculate the resistance measured between the two square ends. Use the given formula.
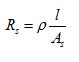
(f) A resistor has a resistance of 30Ω is connected across a battery of emf 8V. Determine:-
i. The current.
ii. The terminal voltage of the battery.
iii. The power delivered by the emf.
iv. The power delivered to the external resistance.
Hire a Professional Essay & Assignment Writer for completing your Academic Assessments
Native Singapore Writers Team
- 100% Plagiarism-Free Essay
- Highest Satisfaction Rate
- Free Revision
- On-Time Delivery
Question 2
(a) State Ohm’s law in your own words.
(b) State Joule’s law in your own words.
(c) Find the equivalent resistance between a and c of the circuit as shown in Figure 2.
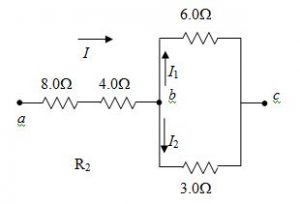
Figure 2
(d) Find the total potential energy of the system of three charges as shown in Figure 3. q1 = 1.00 micro C, q2 = -4.00 micro C and q3 = 3.00 micro C.
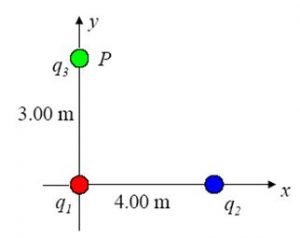
Figure 3
Question 3
(a) An electrical light bulb is rated at 240/80W.
i. What does the rating mean?
ii. The bulb is powered by a 240V direct-current (DC) power supply. Calculate the current flowing through the bulb and its resistance.
(b) State Gauss’ law in your own words.
(c) A charge of 170 micro C is at the centre of a cube of edge 80cm:-
i. Determine the total flux through one face of the cube.
ii. Determine the total flux through the whole surface of the cube.
(d) A cylindrical piece of (neutral) insulating material is placed in an external electric field as shown in Figure 4.
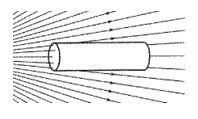
Figure 4
i. What is the net electric flux passing through the surface?
ii. Explain your answer in (i).
Question 4
(a) Faradays’s law of induction can be written as e = ![]()
i. Base on the equation given above, state Faraday’s law in your own words.
ii. Define briefly what are all the terms in the equation.
iii. What is the significance of the negative sign in the equation above?
(b) A magnet moves down through a coil as shown in Figure 5. Sketch and explain what should be the direction of the induced current.
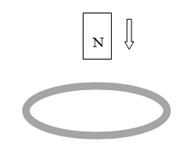
Figure 5
(c) The applied current on a coil is given by Io cos(0.5 pi t) where Io is the maximum current and t is the time in seconds. Sketch the current with respect to time starting at t=0 for two periods of the alternating current. Correctly label the important parameters in the vertical and horizontal axis.
If the induced voltage in the coil due to the current i, is ![]() write the equation for the induced voltage given the current above.
write the equation for the induced voltage given the current above.
Question 5
(a) A circular coil of radius 1cm has 200 turns. It is removed from a magnetic field of 2T in a time of 0.1s. The field direction is normal to the plane of the coil.
i. What is the magnitude of the average voltage induced in the coil?
ii. If the coil is removed more slowly in a time of 1s, what is the magnitude of the voltage induced now?
(b) A conductor located at x = 0.5 m, y = 0 and 0 < z < 2.0 m carries a current of 6.0 A in the direction along the length of the conductor ![]() T. Find the torque about the z-axis.
T. Find the torque about the z-axis.
(c) The equation for the induced field can be written as ![]() , where E(bar) is the induced field, u(bar) is the velocity and B(bar) is the magnetic field. State the two conditions needed for the field E(bar) to be induced.
, where E(bar) is the induced field, u(bar) is the velocity and B(bar) is the magnetic field. State the two conditions needed for the field E(bar) to be induced.
(d) Explain briefly what Maxwell’s equations are used for.
(e) Give four applications of electromagnetic fields.
(f) Maxwell’s equation for Gauss’ law for electric fields is given by ![]() . Light is a form of electromagnetic waves and it also consists of photon particles, where they are no free charges. Demonstrate how this equation can be rewritten to reflect a situation where there are no charges.
. Light is a form of electromagnetic waves and it also consists of photon particles, where they are no free charges. Demonstrate how this equation can be rewritten to reflect a situation where there are no charges.
Get expert homework help in field theory assignment at an affordable price from Singapore Assignment Help. We offer 'solve my assignment' help of field theory. We deliver plagiarism-free work and 100% original content to all assignments at the best price. So hire our assignment writer for Physics assignment help to obtain better grades.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- 7WB52012 Career Research Assignment: Post-MBA Executive Role Analysis and Self-Development Planning
- ACFI3004 Australian Tax Residency & Income Assessment: Heny & Joceline Case Analysis
- CSIT213 Java OOP Assignment 1: ECommerce Management System Implementation Without Collections
- A2369C cGMP Compliance Assignment: Internal Audit CAPA Report for Quality Issues in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- E2419C Health Products Logistics Assignment: Cold Chain & DG Pharma Handling Case Study for Regulatory Compliance in Singapore
- AVET104 Journey Through the Cell Assignment: A Molecular Adventure into Life’s Inner Workings
- Workplace Risk-Based Assessment 1: Evaluation of Hazards, Accidents, and Safety Compliance
- SRM Reflective Assignment 2: Applying Gibbs Model to Overcome Workplace Report Challenges
- ACLP M1P TAE Written Assignment: Skills Framework & Lesson Plan Design Using Gagne’s and Kolb’s Models
- EGH222 Healthcare Analytics Assignment 2: Predictive Model for Sick Days Based on Employee Demographics and Lifestyle Data

