| University | Singapore Management University (SMU) |
| Subject | Macroeconomics |
Overview of task:
Part A: Diagnostics (macroeconomics data collection and interpretations)
Task: You apply knowledge to the macroeconomics data and present a diagnostic analysis of the economy. Make important observations and assess the current situation of the economy; finally, identify if the economy is ‘stable’ or showing any signs of ‘economic downturn’ or any other problem.
Part B: Policy brief report
Task: Based on your ‘Diagnostics’ in Part A, you suggest the ‘Policy Recommendations’. These recommendations must be backed by proper justification and rationale. As a last step, communicate everything (diagnostics, policy recommendations, justification/rationale) effectively to your client in the form of a policy brief. Policy briefs aim to be practical and well-researched to make them useful and worthwhile for your clientele.
Briefing for the (insert decision-makers’ title here. It can be a prime minister!)
Subject: Include a brief but descriptive subject line. (Max length 1 line)
Guide: The subject is the ‘title of your policy brief’.
Executive summary:
Write an executive summary of the policy brief. Your core message should consist of three sentences. The first one provides a summary of the scenario and what you found in Part A. The second sentence summarizes the key rationale for your recommendation. The final sentence summarizes your policy recommendation. Maximum length of 5 lines.
Guide: The statements in this part should stand on their own. Provide specific information and avoid generalities. The reader of your brief should be able to understand the core message without referring to the background information or the rest of the brief.
Hire a Professional Essay & Assignment Writer for completing your Academic Assessments
Native Singapore Writers Team
- 100% Plagiarism-Free Essay
- Highest Satisfaction Rate
- Free Revision
- On-Time Delivery
Recommendations:
Provide minimum 2 to maximum 4 recommendations. Your recommendations can span across two lines. However, a maximum of five lines are permitted for this section.
Guide: Each recommendation should be stated as a clear course of action for the government /organization to pursue. Be precise with your recommendation and the likely impact on the economy but be concise. Avoid generalities and ambiguous statements. Do not explain or seek to justify your recommendation in this section. Do not describe the consequence of your policy recommendation. Do not state conditions or caveats for your recommendation.
Economic rationale:
Begin this section with a short outline of the context for the brief, the summary of the problem identified in Part A, and any other issues that you think useful.
Guide: This should set the scene for the reader and should provide the reader with sufficient background information to understand the purpose of the brief.
Use the remainder of this section to present economic justifications and the rationale behind your recommendation(s). In your discussion, you should;
- highlight any trade-offs entailed in your recommendation(s)
- raise any additional issues if implemented.
- point out the feasibility of the policy implementation (your recommendation(s) need to be realistic)
You can discuss the economic rationale for all your recommendations together or separately for each recommendation. It should be decided by the students as in what format they can present their argument effectively. In the end, narratives should form a logical argument supporting your policy recommendation.
Guide: Incorporate all information required to support your recommendation in this section, regardless of whether or not the same information has been included elsewhere in the brief. Do not assert facts that are unsupported by either the narrative or the diagnostics conducted in section A.
Name of country: United Kingdom
Indicator from Group A: Gross domestic Product
Presentation
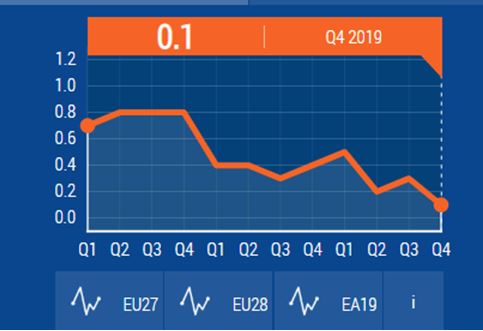
Comments and observations:
According to Partingtonn (2020), the UK economy experienced a downfall in the month of November after there was a fall in consumer spending and decreased manufacturing due to elections. The majority of the sectors of the economy experienced a drop with no exemptions made to the dominant service industry such as hotels. The Office of National Statistics (ONS) reported a 0.3% decline in the GDP in the month of November compared to the previous month due to uncertainty caused by-election(Partington, 2020).
As of the year ended 2017, the GDP was 0.8 where is then rapidly drops to 0.4 for the first quarter of the year 2018. In this period the GDP is steady up to the second Quarter where it then falls shortly to 0.3 in the third quarter. By the end of the fourth quarter, the GDP adjusts backs to 0.4 and slowly picks up to 0.5 by the start of the First Quarter in the year 2019. The rise is later meant by the steep decline in the GDP to 0.2 in the second Quarter that then slowly rises to 0.3 as in the third quarter. The GDP then records a year low of 0.1 GDP. Generally, there is a decline in the country’s GDP.
Indicator from Group B: The unemployment rate
Presentation
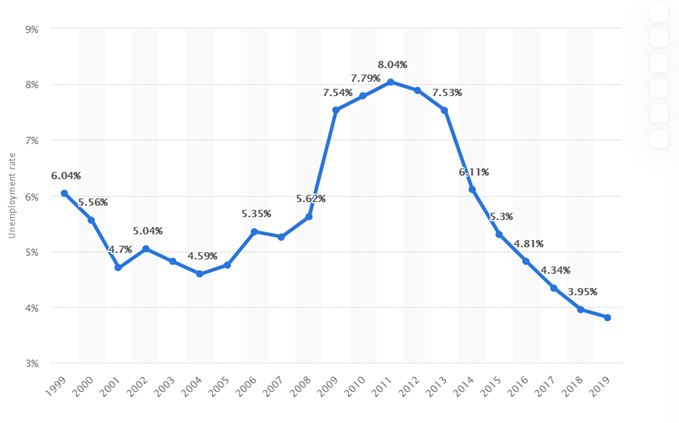
According to Elliot (2019) unemployment rate in the UK is estimated to be about 3.8% with the employment rate known to have risen from 70 to 76%. Unemployment has fallen at a fast rate over r the period of four years and with figures from ONS indicating that the pay growth has fallen back in the three months indicating that the job market may be at its peak. During the third quarter of 2019 (July to September), employment had fallen by 58000 and part-time employment had fallen by 164,000 as the country faced the slowest annual growth in a decade with the heightened with the Brexit uncertainty with the business having to be cautious when hiring (Elliott, 2019).
The rate of unemployment in the UK according to the table for the year 1999 was at 6.04% that then declined to 5.56 % in the year 2000. As of the year ended 2001 the rate of unemployment was at 4.7% that then rose to 5.04% in 2002. The rate of unemployment rate in the UK continued on an up-down trajectory with the year2004 recording as low as 4.95% that then gradually rose to 5.35% as of 2007. There was a small steady increase in the unemployment rate and a top high rate of unemployment of 8.04% was recorded in the year 2011. The rate would then decrease continuously and as of year ended 2019, the rate of unemployment was 3.81%.
We provide experts help with economics assignments to SMU students in completing their economics assignments timely. Our highly qualifies expert online assignment helpers make sure that your macroeconomics assignments are done with utmost priority, thus improving your understanding of macroeconomics. Our help services for international economics assignments are affordable and you can get the maximum value for your money.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- EGH222 Healthcare Analytics Assignment 2: Predictive Model for Sick Days Based on Employee Demographics and Lifestyle Data
- Sustainability Strategy Assignment: Selected Company Case Study on Addressing Sector Challenges and Driving Behavioural Change Campaigns
- 7WBS2012 Executive Career Development Assignment: Career Pathway & Readiness Post-MBA in Education Management
- CVE2322 Gantry Build Prototype Assignment: Sustainable Civil Engineering Model Using Recyclable Materials
- BMG706 Strategic Quality Change Assignment Report: Enhancing Operational Excellence at any Organization
- CVE2323 Structural Analysis Assignment: Matrix Method & STAAD.Pro Evaluation of Frame Systems
- BMK3015 Major Project Assignment: Customer-Centric Design Solutions Using Research & Project Management
- Wellbeing Assignment: University Students’ Perspectives for Improving Mental Health Support
- BCLO001 Business Statistics Assignment: Analysis of Exercise Duration Among Singaporean Students
- BM4364 Customer Experience Assignment: Evaluating CX Practices Through Employee Insights in the Service Industry

